Publication Alert
October 22 2024
This study utilized fiber photometry to explore dorsal striatal calcium and dopamine activity during drug seeking in rats trained on fixed-ratio (FR) or second-order (SO) reinforcement schedules, which represent goal-directed or habit-like cocaine-seeking behavior, respectively. The researchers identified distinct neural activity signatures in the dorsal striatum across these reinforcement conditions.
Key Discussion Points:
- Differential Neural Activity: Rats trained on second-order (habit-like) reinforcement schedules exhibited an enhanced dorsolateral striatum (DLS) dopamine response and a reduced dorsomedial striatum (DMS) calcium response to cue-reinforced lever presses, compared to those trained on fixed-ratio (goal-directed) schedules.
- Cue Extinction Impact: Cue extinction was found to affect calcium and dopamine activity in the dorsomedial striatum (DMS), but not in the dorsolateral striatum (DLS). This indicates that cue extinction alters the neural circuitry underlying goal-directed drug seeking without impacting DLS-dependent, habit-like behavior.
- Thoughts for Discussion: The study mentions recent evidence suggesting that changes in calcium fluorescence detected via fiber photometry, especially in the dorsal striatum, may reflect synaptic activity rather than somatic calcium changes due to the extensive dendritic arborization in this region. This suggests that the observed calcium fluorescence changes could represent a combined effect of excitatory and inhibitory input into dorsal striatal neurons.
Plexon products in this study include:
- Multi-Wavelength Fiber Photometry System (MWPHT): The system was used for in vivo tracking of bulk changes in fluorescent output in the striatal regions of interest during drug-seeking behavior.
This research expands current understanding of the differential roles of the DMS and DLS in goal-directed and habitual behavior, with implications for targeting neural circuits involved in drug-seeking habits. The use of Plexon’s MWPHT system was instrumental in capturing the real-time neural activity patterns that further clarify these mechanisms.
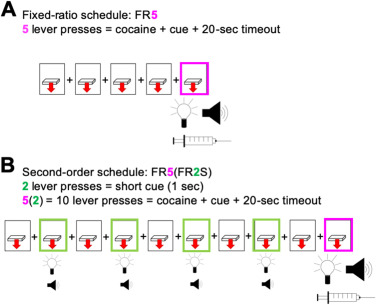
Fig. 1: Schedules of reinforcement. In this example of a fixed-ratio (FR5) schedule of reinforcement, the fifth lever press results in cocaine infusion and a 20-s timeout period during with an audiovisual cue is presented (A). In this example of an FR5(FR2S) second-order (SO) schedule of reinforcement, a brief, 1-s audiovisual stimulus (S) is presented on an FR2 schedule, and upon the fifth completion of the FR2S schedule (after 10 total lever presses), cocaine infusion and the 20-s timeout with audiovisual cue presentation occurs.
For further inquiries about Plexon products or to learn more about our commitment to advancing neuroscience research, please visit our website or contact our dedicated team at info@plexon.com